Introduction
In the world of investment strategies, covered calls represent a popular approach for investors looking to generate additional income from their stock holdings. This options strategy involves owning shares of a stock while simultaneously selling call options against those shares. For high-volatility stocks like Tesla (TSLA), covered calls can be particularly intriguing due to the potentially lucrative option premiums.
In this blog, we'll dive into our findings from simulating monthly covered calls on Tesla, comparing the results against a simple buy-and-hold approach. We'll explore everything from data collection methodology to performance metrics and visual insights that reveal the true nature of this income-generating strategy.
Covered Call Strategy Explained
A covered call strategy combines two positions: owning shares of a stock (in this case, Tesla) and selling call options against those shares. When you sell a call option, you receive an upfront premium payment in exchange for agreeing to sell your shares at a predetermined price (the strike price) if the stock rises above that level by the option's expiration date.
The primary goals of implementing a covered call strategy are twofold: generating consistent income through option premiums and providing partial downside protection. The premium you receive effectively lowers your cost basis in the stock, offering a small buffer against price declines. However, this comes with a significant trade-off – your potential gains are capped if the stock price rises substantially above your option's strike price.
Data Collection and Simulation Setup
To ensure our analysis was grounded in reality, we collected historical data on Tesla stock from July 2024 to July 2025. This included daily price data, volatility metrics, and options pricing information. For stock price data, we utilized reliable financial data sources. For options data, we employed the Black-Scholes model to estimate at-the-money call option premiums based on Tesla's historical volatility patterns.
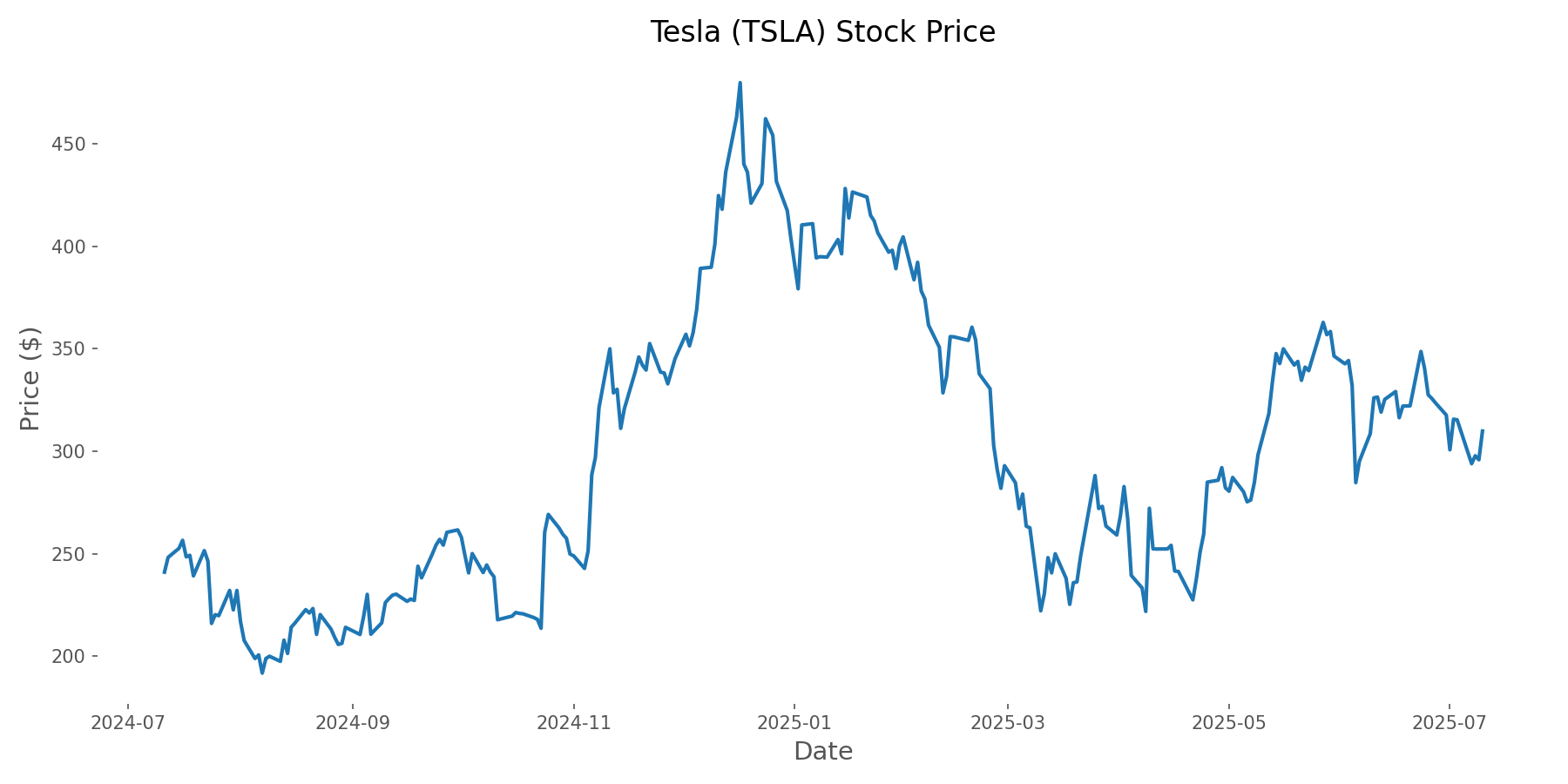
Our simulation was built on several key assumptions to create a realistic model of a covered call strategy. We implemented monthly selling of at-the-money call options, assuming ownership of 100 shares of Tesla stock per contract (the standard contract size). The simulation began with an initial investment of $100,000 in Tesla shares on July 11, 2024, when Tesla was trading at $241.03 per share.
Throughout the simulation, we tracked key metrics: total returns, premium income, portfolio volatility, and risk-adjusted performance measures. This approach allowed us to evaluate both the raw returns and risk characteristics of each strategy.
Analysis and Data Visualization
Our analysis revealed several fascinating insights about implementing a covered call strategy on Tesla stock. Let's explore the key findings through data visualizations that tell the story of how these strategies performed.
Portfolio Performance Comparison
The most fundamental question is how the covered call strategy performed compared to simply holding Tesla stock. As shown in the chart below, during our study period, the buy-and-hold approach outperformed the covered call strategy in terms of total return. The buy-and-hold strategy delivered a 28.56% return, while the covered call strategy returned just 0.97%.
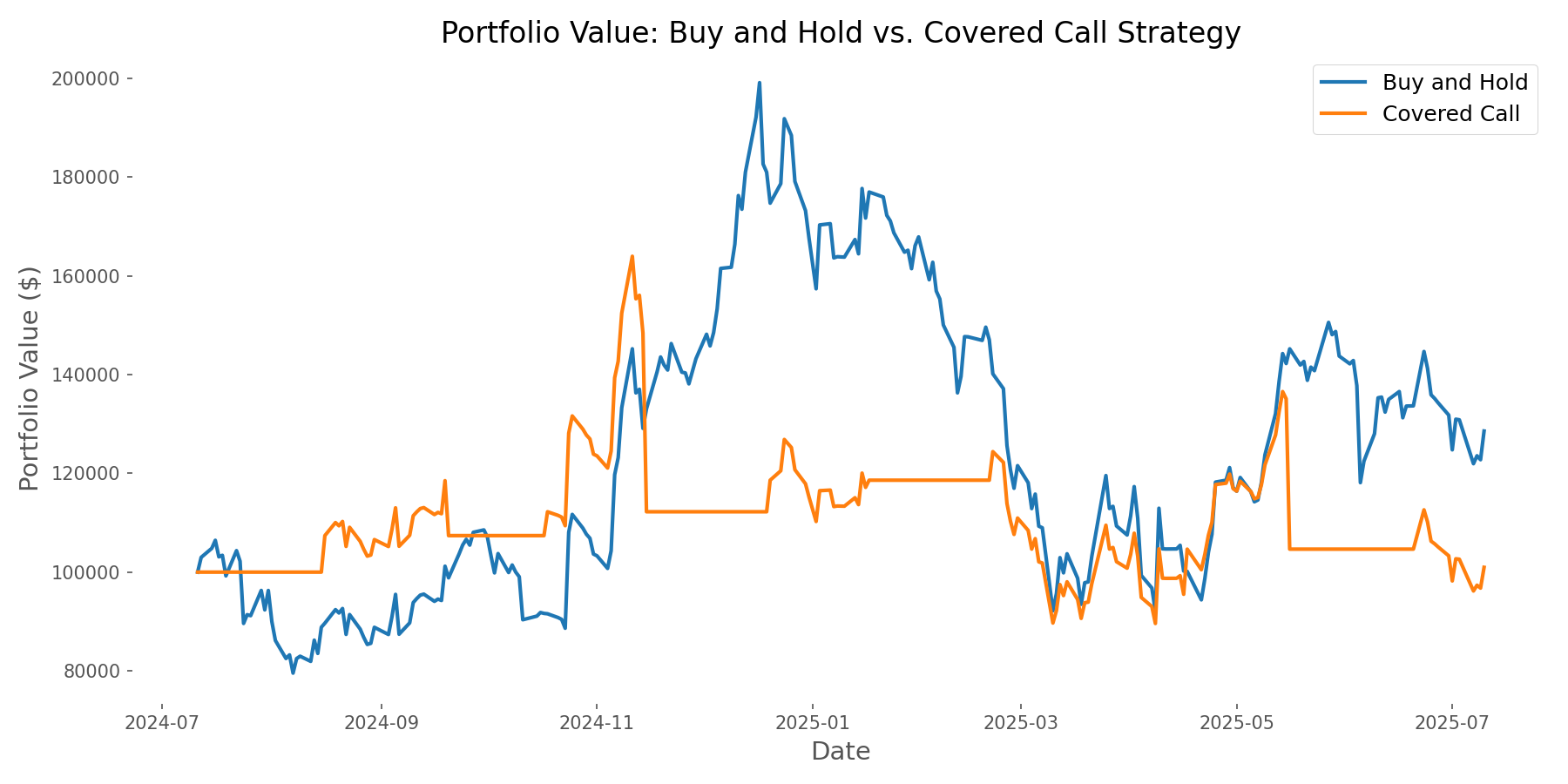
This performance gap illustrates a key trade-off of covered calls – in bullish markets, the strategy's capped upside can result in opportunity costs. During this period, Tesla's strong upward movement benefited the buy-and-hold approach while limiting the covered call strategy's gains.
Premium Income Generation
Despite the underperformance in total return, the covered call strategy excelled at its primary objective: generating income. Over the one-year period, the strategy produced $33,583 in option premium income, representing an impressive 33.58% of the initial investment.
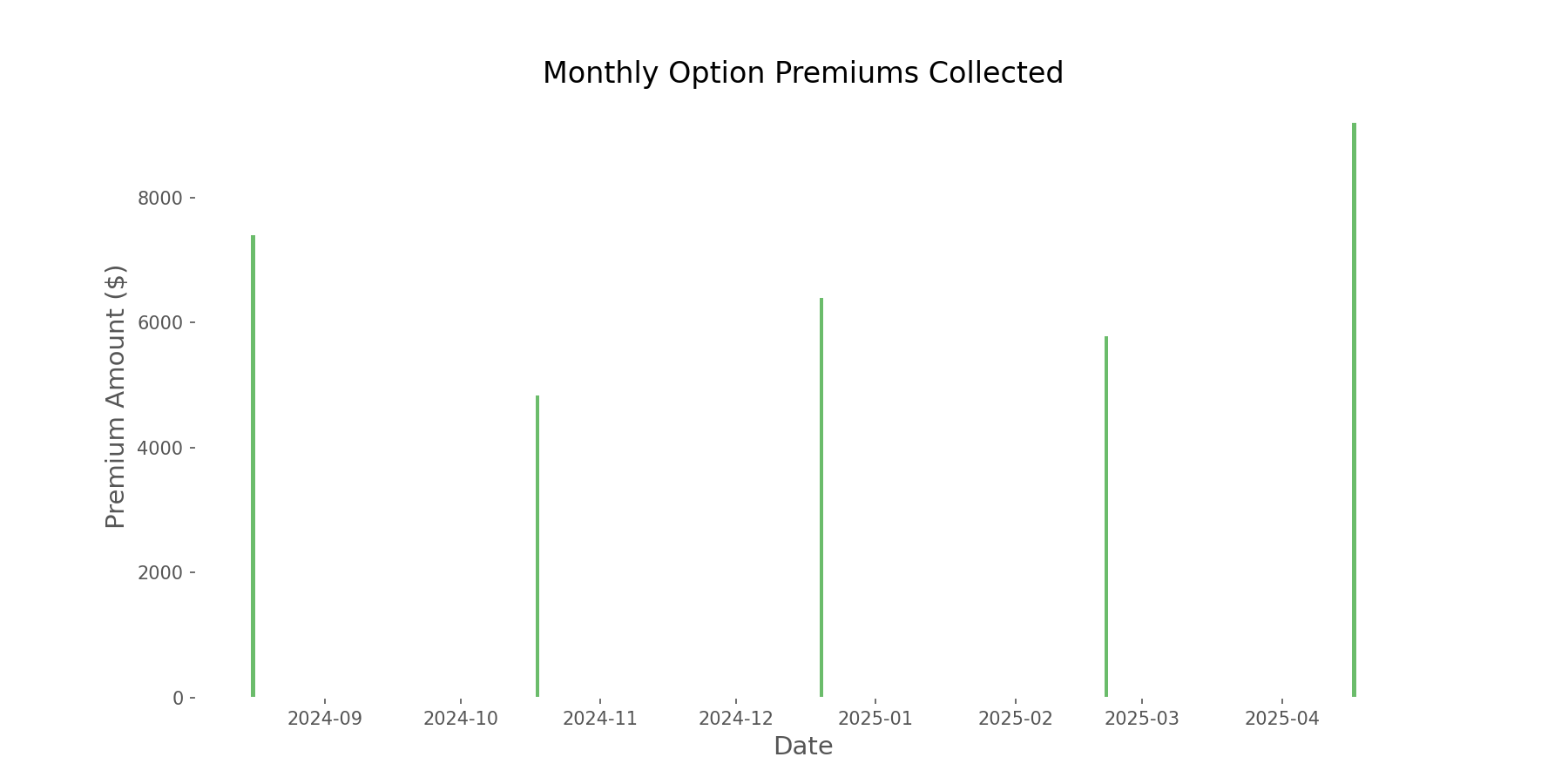
Risk Reduction Benefits
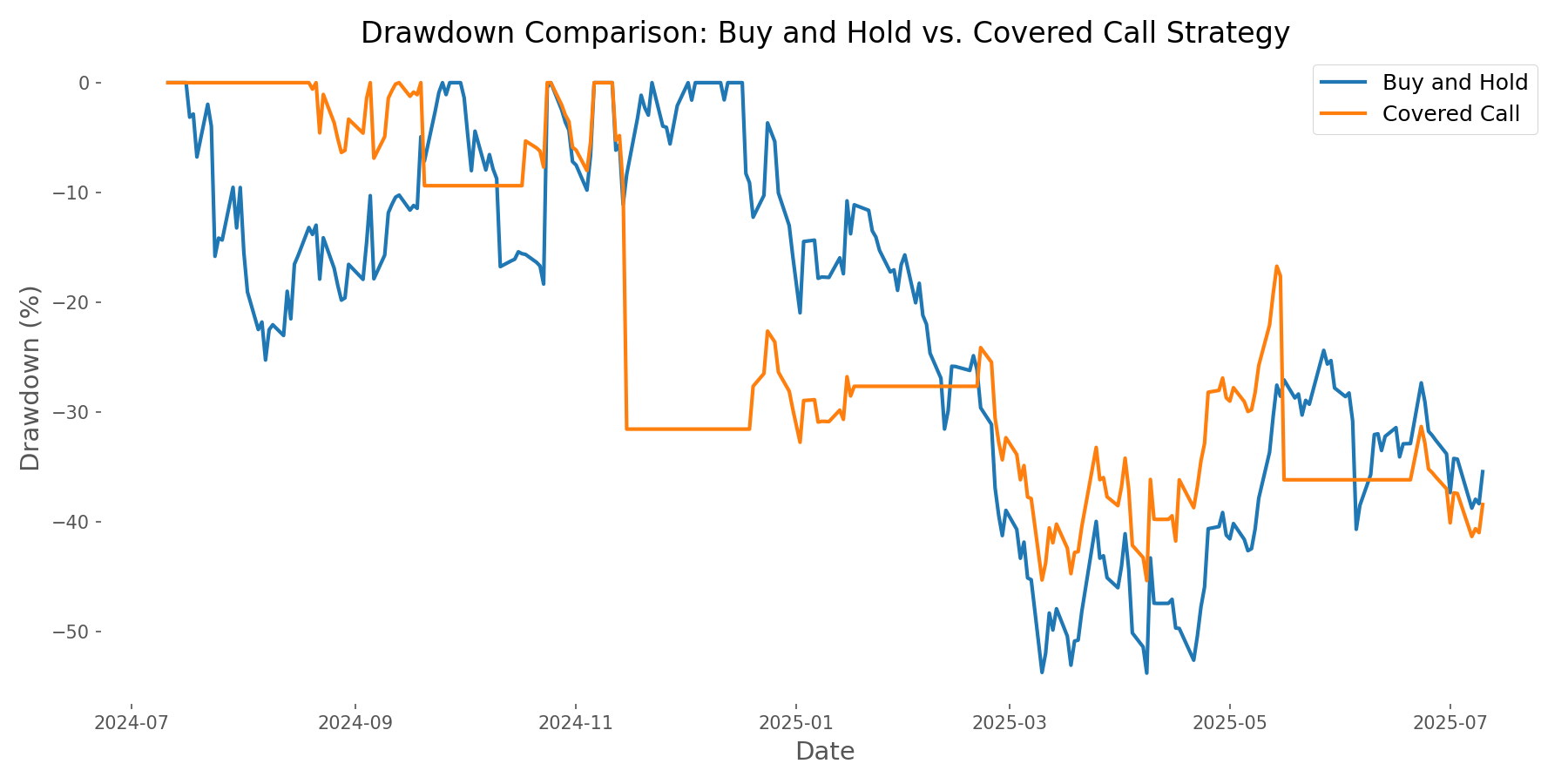
One compelling advantage of the covered call strategy was its superior risk profile. The approach demonstrated better downside protection with a maximum drawdown of -45.34% compared to -53.77% for buy-and-hold. Additionally, the covered call strategy exhibited lower annualized volatility (61.28% vs. 73.89%).
Volatility and Premium Relationship
Our analysis found a strong correlation (0.859) between Tesla's stock volatility and option premiums. This relationship is visualized below, showing how higher volatility corresponded with higher premium income.
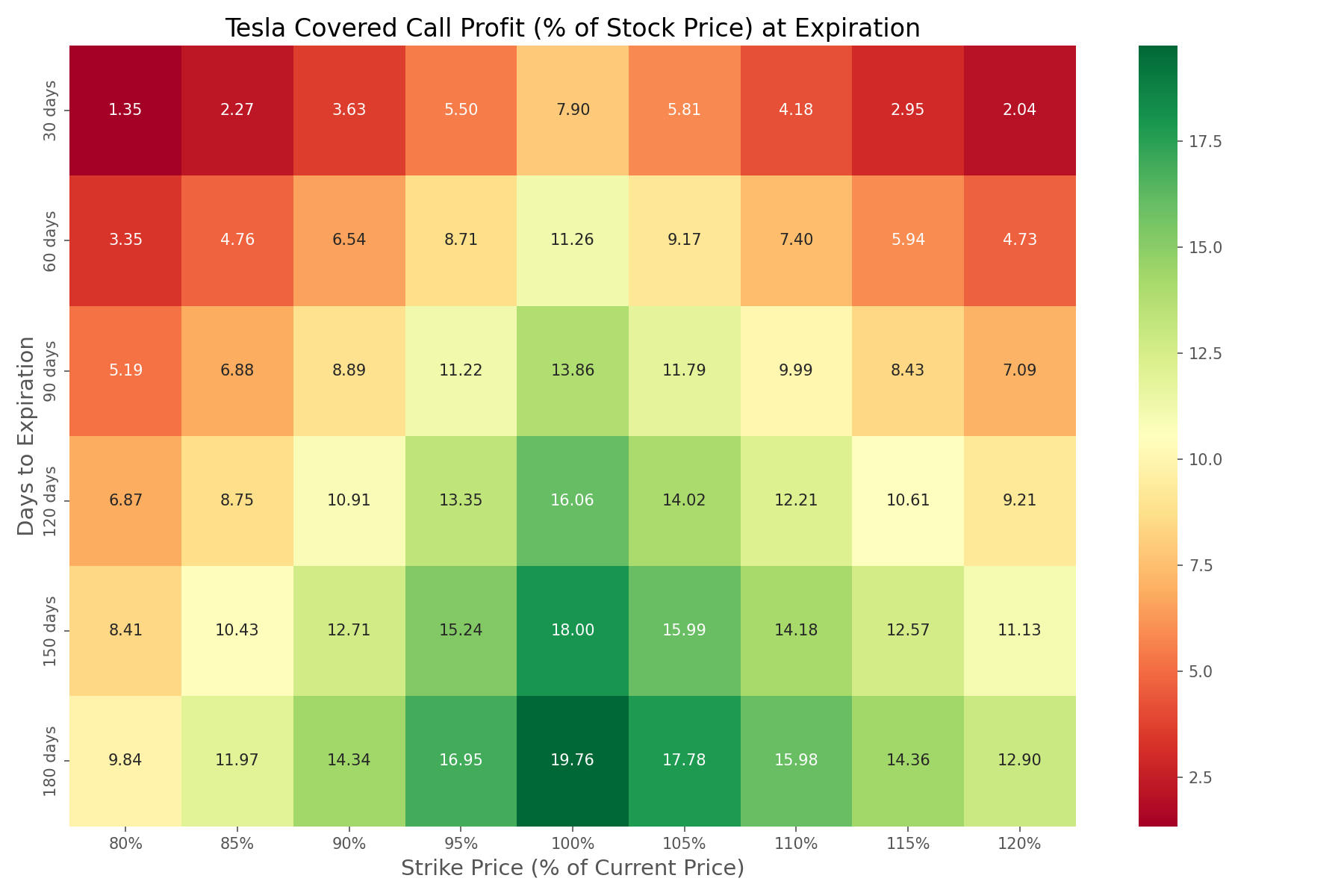
Optimizing Strike Prices and Expirations
To provide deeper insights into strategy optimization, we created heatmaps illustrating the profitability of different combinations of strike prices and expiration dates. These visualizations help identify the most promising parameters for implementing a covered call strategy on Tesla.
Conclusion and Investor Insights
Our data-driven analysis of implementing a covered call strategy on Tesla stock reveals a nuanced picture with important implications for different types of investors. While the buy-and-hold approach outperformed during this period of strong upward price movement (28.56% vs. 0.97%), the covered call strategy demonstrated significant advantages in terms of income generation and risk reduction.
The strategy generated substantial premium income (33.58% of initial investment) and provided better downside protection with lower maximum drawdown and reduced volatility. For investors considering this strategy, we recommend analyzing the trade-offs between premium income and potential capital appreciation based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!